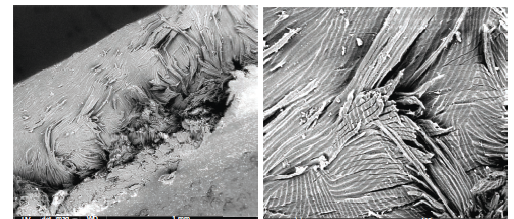
Abstract Two hard botanical structures have been characterised in terms of mechanics and structure: the pseudofruit of Coix lacryma-jobi, a native plant of Southeast Asia, and the kernel of the drupe fruit of Thevetia peruviana, a native plant of tropical America. Two indentation techniques at different scales (micro and nano) were employed. […]
BioDent
Abstract In the present study, the possibility that a diabetic (DM) status might worsen age-related bone deterioration was explored in mice. Male CD-1 mice aged 2 (young control group) or 16 months, nondiabetic or made diabetic by streptozotocin injections, were used. DM induced a decrease in bone volume, trabecular number, […]
Abstract Type 2 diabetes (T2D) incidence in adolescents is rising and may interfere with peak bone mass acquisition. We tested the effects of early-onset T2D on bone mass, microarchitecture, and strength in the TALLYHO/JngJ mouse, which develops T2D by 8 weeks of age. We assessed metabolism and skeletal acquisition in […]
Abstract Osteoporosis is a silent disease, characterized by a porous bone micro-structure that enhances risk for fractures and associated disabilities. Senile, or age-related osteoporosis (SO), affects both men and women, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality. However, cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying senile osteoporosis are not fully known. Recent studies […]
Abstract The reference point indentation (RPI) method is a microindentation technique involving successive indentation cycles. We employed RPI to measure average stiffness (Ave US), indentation distance increase (IDI), total indentation distance (TID), average energy dissipated (Ave ED), and creep indentation distance (CID) of swine femoral cortical bone (mid-diaphysis) as a […]
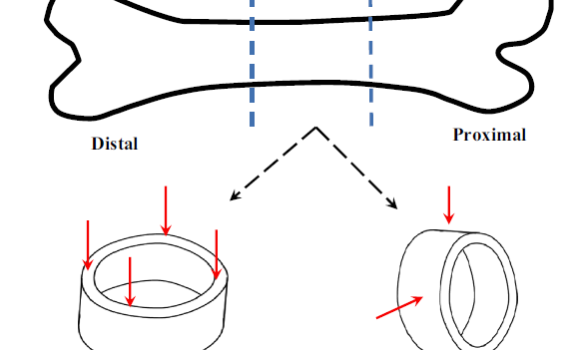
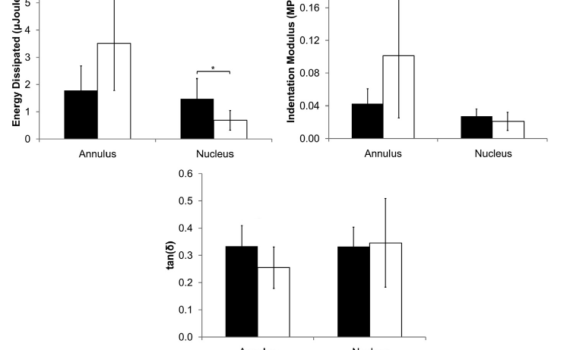
Abstract BACKGROUND CONTEXT: It is well-established that disc mechanical properties degrade with degeneration. However, prior studies utilized cadaveric tissues from donors with undefined back pain history. Disc degeneration may present with pain at the affected motion segment, or it may be present in the absence of back pain. The mechanical […]
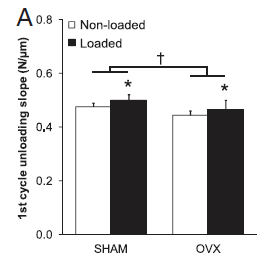
Abstract Exercise that mechanically loads the skeleton is advocated when young to enhance lifelong bone health. Whether the skeletal benefits of elevated loading when young persist into adulthood and after menopause are important questions. This study investigated the influence of a surgically induced menopause in female Sprague-Dawley rats on the […]
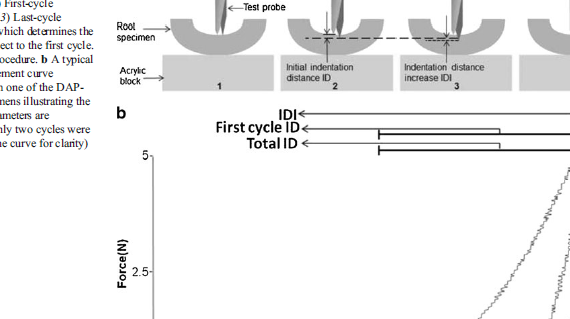
Abstract OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to investigate the capability of a novel reference point indentation apparatus to test the indentation properties of root canal surface dentine treated with three intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Immature human premolars were selected (n = 22). Four […]
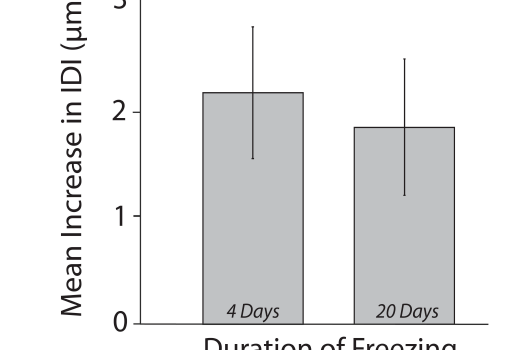
Abstract he serious health risks posed by bone fractures create a growing need for accurately diagnosing fracture risk. The Reference Point Indentation instrument (RPI) directly measures key mechanical properties in vivo to assess bone fracturability. There is a wealth of information that could be obtained from measuring cryopreserved bone samples […]
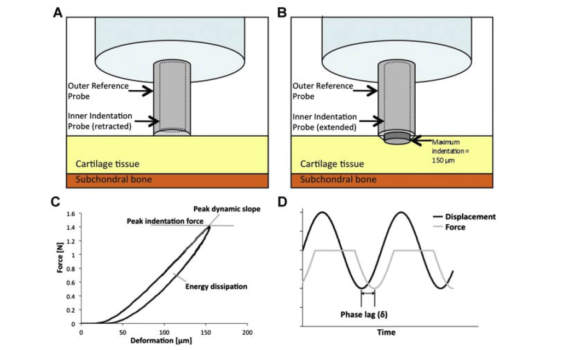
Abstract The objective of this study is to examine the local relationship between T(1ρ) relaxation times and the mechanical behavior of human osteoarthritic articular cartilage using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and local in situ microindentation. Seven human tibial plateaus were obtained from patients who underwent total knee arthroplasty due […]